In Vitro Fertilization(IVF), the Assisted Reproductive Technology is commonly known as ‘Test Tube Baby’.
In normal pregnancy, (natural conception) the fertilization takes place inside a women’s body and then the fertilized egg attaches itself to the inner lining of the womb (uterine wall), and continues to grow into a baby.
IVF is recommended for the women who struggle to conceive naturally.
Here, the fertilization of the eggs take place in a laboratory dish, and then the fertilized eggs (embryos) are transferred into the woman’s uterus.
Basic Steps for IVF
Step 1: Ovarian Stimulation
Fertility drugs (contains follicle stimulating hormones) are given to stimulate egg production. So that ovaries can produce more eggs than normal. (Woman typically produces only one egg per month).
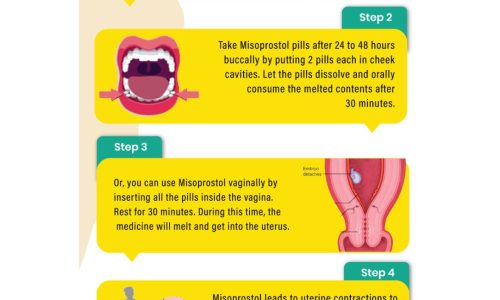
Step 2: Egg Retrieval
A minor surgery called Follicular aspiration is performed to collect the eggs from the ovary.
A thin needle connected to a suction device is inserted through vagina into the ovary to suck the eggs out.
Step 3: Sperm Collection
Sperm sample is collected and prepared to combine with the eggs.
Step 4: Insemination and Fertilization
The collected eggs and sperms are mixed together in a laboratory dish, nestled . inside an incubator (temperature control). Fertilization takes place within few hours
ICSI technique (direct injection of sperm into egg) is performed for severe male factor infertility.
Step 5: Embryo Transfer
The fertilized eggs called zygotes divides and develop into embryos which are then transferred into the womb. The embryos are transferred by inserting a catheter (containing embryos) into the uterus through the vagina. The embryo attaches to the inner lining of the womb embryo growth begins. (uterus wall), and the healthy embryo growth begins.
Usually 2 or 3 embryos are transferred during IVF, which can lead to multiple pregnancies However, patients can choose Elective Single Embryo Transfer (eSET) opt, where one embryo can be transferred into the uterus, rather than multiple.

![]()